Mazda Training manual — part 6

Powertrain Engines
Balancer Shaft Unit
•
The balancer shafts minimize the engine vibrations by rotating at twice the speed of the
crankshaft.
•
The balancer shaft unit features a two-piece housing, which is fixed to the cylinder block
by four bolts.
NOTE: The balancer shaft unit cannot be repaired due to its precise interior construction, i.e.
it must be replaced as a complete unit.
•
If the cylinder block, crankshaft, crankshaft main bearing, or balancer shaft unit have
been replaced, the backlash between the drive gear of the crankshaft and the driven
gear of the balancer shaft unit must be adjusted using shims (refer to the workshop
manual for details).
L1001.4_01006
1
Adjustment shim
6
Counter weights
2
Engraved identification mark
7
Balancer shaft unit housing
3
Drive gear
8
Engine front side
4 Balancer
shaft
no.2
9 Crankshaft
5
Balancer shaft no.1 with driven gear
Curriculum Training
01-11
Engines Powertrain
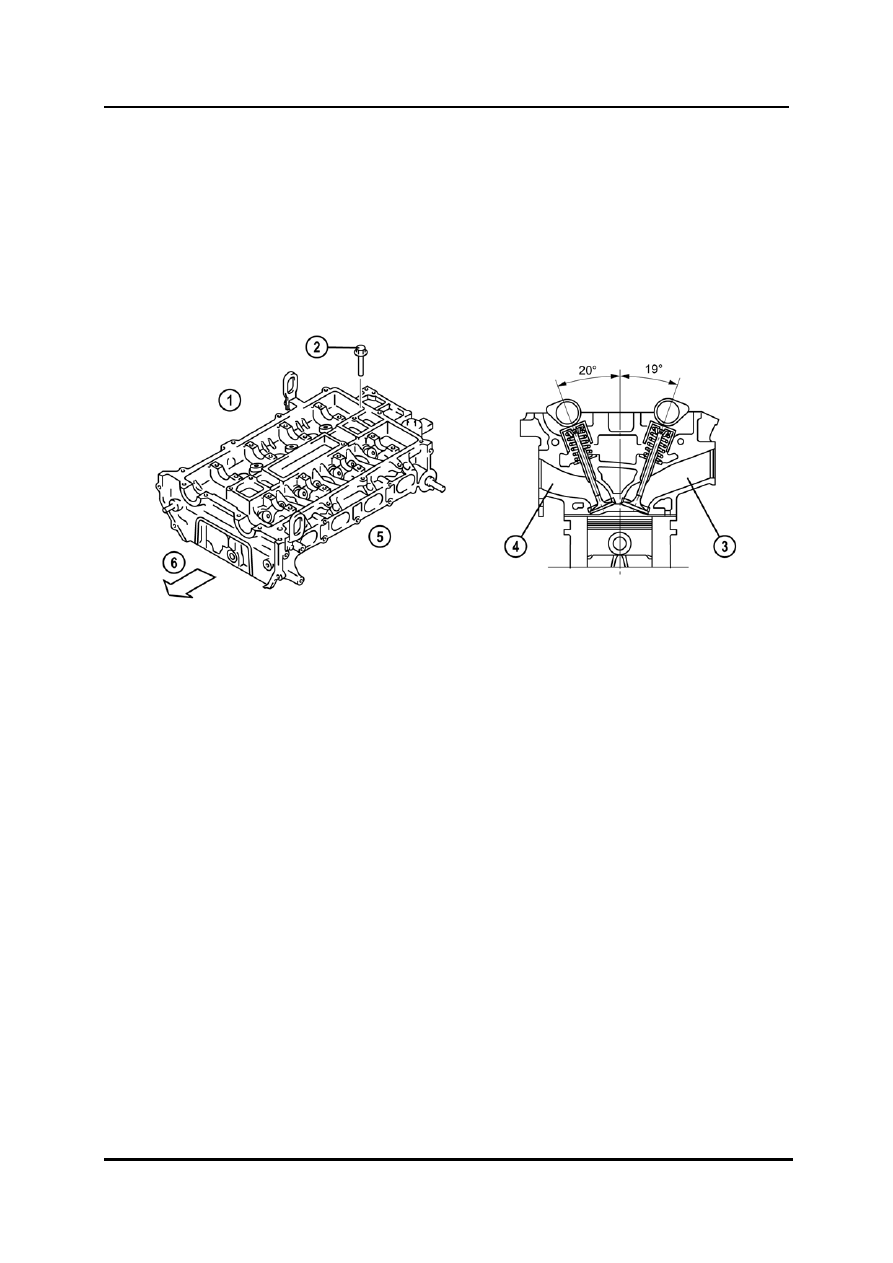
Cylinder Head
•
The cylinder head is a conventional construction with separate camshaft bearing caps.
•
The cylinder head bolts are torque-to-yield bolts, which must be tightened in several
stages (refer to the workshop manual for details).
NOTE: The cylinder head bolts must not be re-used if their length exceeds the specification
(refer to the workshop manual for details).
L1001.4_01007
1
Exhaust side
4
Exhaust port
2
Cylinder head bolt
5
Intake side
3
Intake port
6
Engine front side
01-12 Curriculum
Training
Powertrain Engines
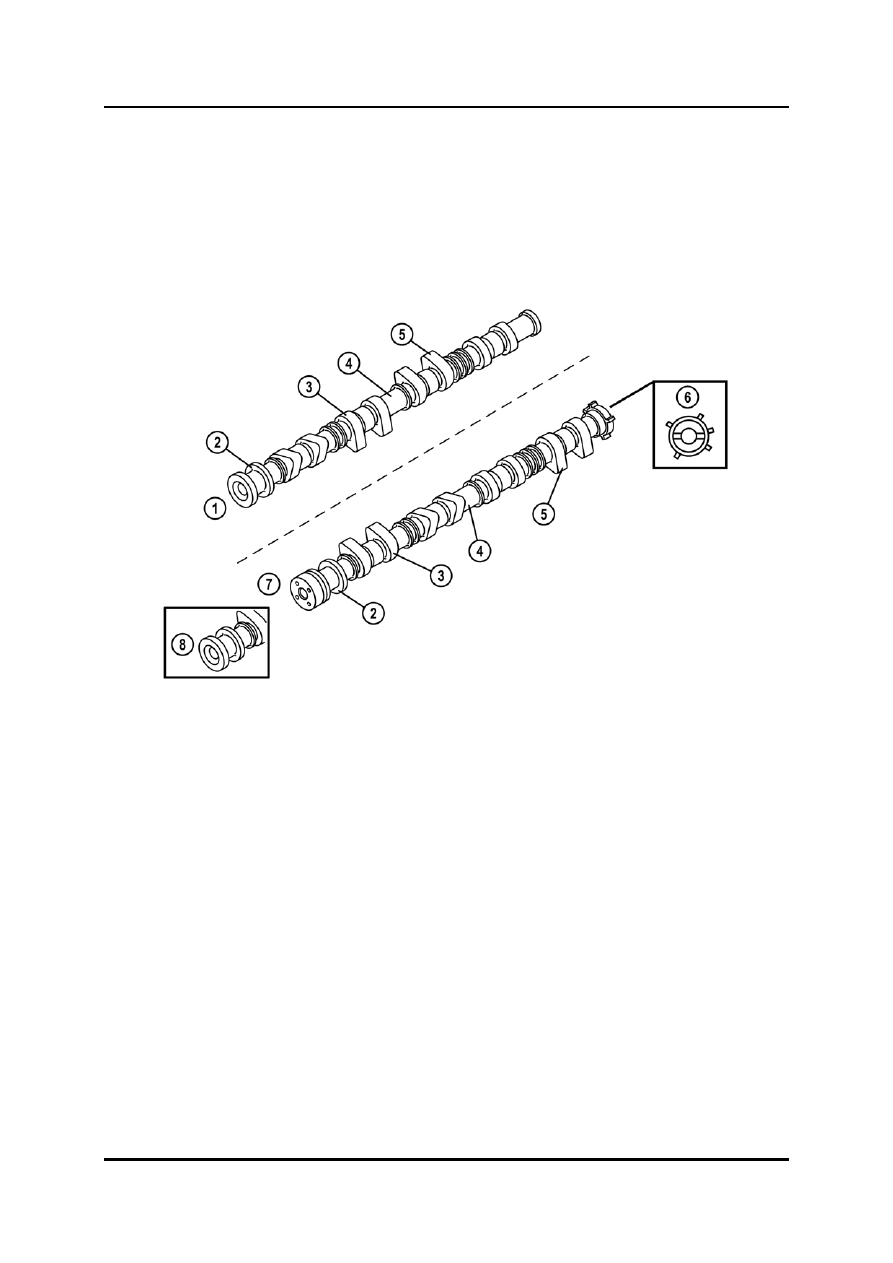
Camshafts
•
The camshafts feature no key for the installation of the camshaft sprockets, i.e. solely
the clamping force of the lock bolt secures the sprocket on the camshaft.
•
The intake camshaft of the LF and L3 engine is equipped with an oil line supplying oil to
the camshaft actuator of the variable valve timing system.
•
The intake camshaft has a pulse wheel for the CMP (Camshaft Position) sensor signals.
L1001.4_01008
1
Exhaust camshaft
5
Cam nose
2
Thrust collar
6
Pulse wheel for CMP sensor
3
Cam heel
7
Intake camshaft
(with variable valve timing system)
4
Cam journal
8
Intake camshaft front end (without
variable valve timing system)
Curriculum Training
01-13

Engines Powertrain
Valve Actuation
•
The camshafts actuate the valves via mechanical bucket tappets without adjustment
shims.
•
The valve clearance is adjusted by the different thickness of the bucket tappets. The
tappet thickness can be determined by the engraved number (e.g. number “402” means
a thickness of 3.402 mm). In order to replace the tappets the camshafts have to be
removed (refer to the workshop manual for details).
•
The valve clearance has to be audibly inspected (and if noisy adjusted) every 120,000
km.
L1001.4_01009
1 Camshaft
4 Tappet
thickness
2 Tappet
cross-sectional
view
5
Valve stem contact surface
3
Cam lobe contact surface
6
Bucket tappet
01-14 Curriculum
Training

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст