Ford Ranger (2022 year). Manual in english — page 19

B-pillar:
The structural member
at the side of the vehicle behind
the front door.
*
Bead area of the tire:
Area of
the tire next to the rim.
*
Sidewall of the tire:
Area
between the bead area and the
tread.
*
Tread area of the tire:
Area of
the perimeter of the tire that
contacts the road when mounted
on the vehicle.
*
Rim:
The metal support (wheel)
for a tire or a tire and tube
assembly upon which the tire
beads are seated.
Information Contained on the
Tire Sidewall
Both United States and Canada
Federal regulations require tire
manufacturers to place
standardized information on the
sidewall of all tires. This
information identifies and
describes the fundamental
characteristics of the tire and also
provides a U.S. DOT Tire
Identification Number for safety
standard certification and in case
of a recall.
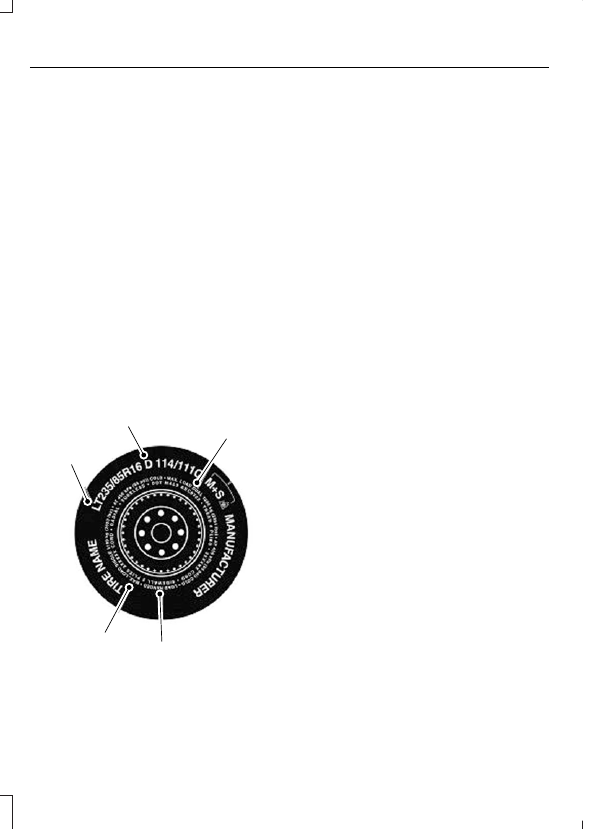
Information on P Type Tires
H
I
J
K
L
M
A
B
C D
E
F
G
E142543
P215/65R15 95H is an example of
a tire size, load index and speed
rating. The definitions of these
items are listed below. (Note that
the tire size, load index and speed
rating for your vehicle could be
different from this example.)
A.
P:
Indicates a tire, designated
by the Tire and Rim Association,
that could be used for service on
cars, sport utility vehicles,
minivans and light trucks.
Note:
If
your tire size does not begin with
a letter this could mean it is
designated by either the European
Tire and Rim Technical
Organization or the Japan Tire
Manufacturing Association.
295
Wheels and Tires
B.
215:
Indicates the nominal
width of the tire in millimeters
from sidewall edge to sidewall
edge. In general, the larger the
number, the wider the tire.
C.
65:
Indicates the aspect ratio
which gives the tire's ratio of
height to width.
D.
R:
Indicates a radial type tire.
E.
15:
Indicates the wheel or rim
diameter in inches. If you change
your wheel size, you will have to
purchase new tires to match the
new wheel diameter.
F.
95:
Indicates the tire's load
index. It is an index that relates to
how much weight a tire can carry.
You could find this information in
your owner’s manual. If not,
contact a local tire dealer.
Note:
This information will not be
included on all tires because it is
not required by federal law.
G.
H:
Indicates the tire's speed
rating. The speed rating denotes
the speed at which a tire is
designed to be driven for extended
periods of time under a standard
condition of load and inflation
pressure. The tires on your vehicle
could operate at different
conditions for load and inflation
pressure. These speed ratings
could need to be adjusted for the
difference in conditions. The
ratings range from 81 mph
(130 km/h) to 186 mph
(299 km/h). These ratings are
listed in the following chart.
Note:
This information will not be
included on all tires because it is
not required by federal law.
mph ( km/h)
Letter
rating
81 (130)
M
87 (140)
N
99 (159)
Q
106 (171)
R
112 (180)
S
118 (190)
T
124 (200)
U
130 (210)
H
149 (240)
V
168 (270)
W
186 (299)
Y
Note:
For tires with a maximum
speed capability over 149 mph
(240 km/h), tire manufacturers
sometimes use the letters ZR. For
those with a maximum speed
capability over 186 mph
(299 km/h), tire manufacturers
always use the letters ZR.
H.
U.S. DOT Tire Identification
Number:
This begins with the
letters DOT and indicates that the
tire meets all federal standards.
The next two numbers or letters
are the plant code designating
where it was manufactured, the
next two are the tire size code and
296
Wheels and Tires
the last four numbers represent
the week and year the tire was
built. For example, the numbers
317 mean the 31st week of 1997.
After 2000 the numbers go to four
digits. For example, 2501 means
the 25th week of 2001. The
numbers in between are
identification codes used for
traceability. This information is
used to contact customers if a tire
defect requires a recall.
I.
M+S or M/S:
Mud and Snow, or
AT:
All Terrain, or
AS:
All Season.
J.
Tire Ply Composition and
Material Used:
Indicates the
number of plies or the number of
layers of rubber-coated fabric in
the tire tread and sidewall. Tire
manufacturers also must indicate
the ply materials in the tire and the
sidewall, which include steel,
nylon, polyester, and others.
K.
Maximum Load:
Indicates the
maximum load in kilograms and
pounds that can be carried by the
tire (affixed to either the door
hinge pillar, door-latch post, or the
door edge that meets the
door-latch post, next to the
driver's seating position), or Tire
Label located on the B-pillar or
the edge of the driver's door.
L.
Treadwear, Traction and
Temperature Grades:
*
Treadwear:
The treadwear
grade is a comparative rating
based on the wear rate of the tire
when tested under controlled
conditions on a specified
government test course. For
example, a tire graded 150 would
wear 1½ times as well on the
government course as a tire
graded 100.
*
Traction:
The traction grades,
from highest to lowest are AA, A,
B, and C. The grades represent the
tire's ability to stop on wet
pavement as measured under
controlled conditions on specified
government test surfaces of
asphalt and concrete. A tire
marked C could have poor traction
performance.
*
Temperature:
The temperature
grades are A (the highest), B and
C, representing the tire's
resistance to the generation of
heat and its ability to dissipate
heat when tested under controlled
conditions on a specified indoor
laboratory test wheel.
M.
Maximum Inflation
Pressure:
Indicates the tire
manufacturers' maximum
permissible pressure or the
pressure at which the maximum
load can be carried by the tire. This
pressure is normally higher than
the vehicle manufacturer's
recommended cold inflation
pressure which can be found on
the Safety Compliance
Certification Label (affixed to
either the door hinge pillar,
297
Wheels and Tires
door-latch post, or the door edge
that meets the door-latch post,
next to the driver's seating
position), or Tire Label located on
the B-pillar or the edge of the
driver's door. The cold inflation
pressure should never be set lower
than the recommended pressure
on the vehicle label.
The tire suppliers could have
additional markings, notes or
warnings such as standard load
or radial tubeless.
Additional Information
Contained on the Tire Sidewall
for LT Type Tires
Note:
Tire Quality Grades do not
apply to this type of tire.
A
B
C
B
D
E142544
LT type tires have some additional
information beyond those of P
type tires. These differences are
described below.
A.
LT:
Indicates a tire, designated
by the Tire and Rim Association,
that is intended for service on light
trucks.
B.
Load Range and Load
Inflation Limits:
Indicates the
tire's load-carrying capabilities
and its inflation limits.
C.
Maximum Load Dual lb (kg)
at psi (kPa) cold:
Indicates the
maximum load and tire pressure
when the tire is used as a dual;
defined as four tires on the rear
axle (a total of six or more tires on
the vehicle).
D.
Maximum Load Single lb
(kg) at psi (kPa) cold:
Indicates
the maximum load and tire
pressure when the tire is used as
a single; defined as two tires
(total) on the rear axle.
Information on T Type Tires
T145/80D16 is an example of a
tire size.
Note:
The temporary tire size for
your vehicle could be different from
this example. Tire Quality Grades
do not apply to this type of tire.
298
Wheels and Tires
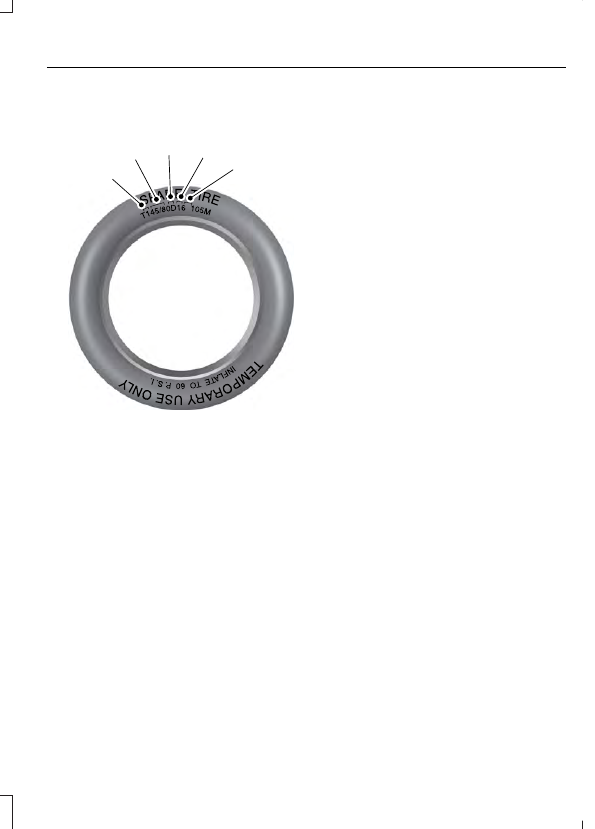

A
B
C
D
E
E142545
T type tires have some additional
information beyond those of P
type tires. These differences are
described below:
A.
T:
Indicates a type of tire,
designated by the Tire and Rim
Association, that is intended for
temporary service on cars, sport
utility vehicles, minivans and light
trucks.
B.
145:
Indicates the nominal
width of the tire in millimeters
from sidewall edge to sidewall
edge. In general, the larger the
number, the wider the tire.
C.
80:
Indicates the aspect ratio
which gives the tire's ratio of
height to width. Numbers of 70 or
lower indicate a short sidewall.
D.
D:
Indicates a diagonal type tire.
R:
Indicates a radial type tire.
E.
16:
Indicates the wheel or rim
diameter in inches. If you change
your wheel size, you will have to
purchase new tires to match the
new wheel diameter.
Location of the Tire Label
You will find a Tire Label
containing tire inflation pressure
by tire size and other important
information located on the B-Pillar
or the edge of the driver's door.
See
Inflating Your Tires
Safe operation of your vehicle
requires that your tires are
properly inflated. Remember that
a tire can lose up to half of its air
pressure without appearing flat.
Every day before you drive, check
your tires. If one looks lower than
the others, use a tire gauge to
check pressure of all tires and
adjust if required.
At least once a month and before
long trips, inspect each tire and
check the tire pressure with a tire
gauge (including spare, if
equipped). Inflate all tires to the
inflation pressure recommended
by us.
299
Wheels and Tires
You are strongly urged to buy a
reliable tire pressure gauge, as
automatic service station gauges
could be inaccurate. We
recommend the use of a digital or
dial-type tire pressure gauge
rather than a stick-type tire
pressure gauge.
Use the recommended cold
inflation pressure for optimum tire
performance and wear.
Under-inflation or over-inflation
could cause uneven treadwear
patterns.
WARNING:
Under-inflation
is the most common cause of
tire failures and may result in
severe tire cracking, tread
separation or blowout, with
unexpected loss of vehicle
control and increased risk of
injury. Under-inflation increases
sidewall flexing and rolling
resistance, resulting in heat
buildup and internal damage to
the tire. It also may result in
unnecessary tire stress, irregular
wear, loss of vehicle control and
accidents. A tire can lose up to
half of its air pressure and not
appear to be flat!
Always inflate your tires to our
recommended inflation pressure
even if it is less than the maximum
inflation pressure information
found on the tire. Our
recommended tire inflation
pressure is found on the Safety
Compliance Certification Label or
Tire Label (affixed to either the
door hinge pillar, door-latch post,
or the door edge that meets the
door-latch post, next to the
driver's seating position), or Tire
Label located on the B-pillar or
the edge of the driver's door.
Failure to follow the tire pressure
recommendations can cause
uneven treadwear patterns and
adversely affect the way your
vehicle handles.
Note:
Do not reduce tire pressure
to change the ride characteristics
of the vehicle. If you do not
maintain the inflation pressure at
the levels specified by us, your
vehicle could experience a
condition known as shimmy.
Shimmy is a severe vibration and
oscillation in the steering wheel
after the vehicle travels over a
bump or dip in the road that does
not dampen out by itself. Shimmy
could result from significant
under-inflation of the tires,
improper tires (load range, size, or
type), or vehicle modifications such
as lift-kits. In the event that your
vehicle experiences shimmy, you
should slowly reduce speed by
either lifting off the accelerator
pedal or lightly applying the brakes.
The shimmy will cease as the
vehicle speed decreases.
Maximum Inflation Pressure
is
the tire manufacturer's maximum
permissible pressure and the
pressure at which the maximum
load can be carried by the tire. This
pressure is normally higher than
300
Wheels and Tires
the manufacturer’s recommended
cold inflation pressure which can
be found on the Safety
Compliance Certification Label
(affixed to either the door hinge
pillar, door-latch post, or the door
edge that meets the door-latch
post, next to the driver's seating
position), or Tire Label located on
the B-pillar or the edge of the
driver's door. The cold inflation
pressure should never be set lower
than the recommended pressure
on the Safety Compliance
Certification Label or Tire Label.
When weather temperature
changes occur, tire inflation
pressures also change. A 10°F
(6°C) temperature drop can
cause a corresponding drop of 1
psi (7 kPa) in inflation pressure.
Check your tire pressures
frequently and adjust them to the
proper pressure which can be
found on the Safety Compliance
Certification Label or Tire Label.
To check the pressure in your
tire(s):
1. Make sure the tires are cool,
meaning they are not hot from
driving even a mile.
Note:
If you are checking tire
pressure when the tire is hot, (for
example, driven more than 1 mile
[1.6 kilometers]), never bleed or
reduce air pressure. The tires are
hot from driving and it is normal for
pressures to increase above
recommended cold pressures. A
hot tire at or below recommended
cold inflation pressure could be
significantly under-inflated.
Note:
If you have to drive a
distance to get air for your tire(s),
check and record the tire pressure
first and add the appropriate air
pressure when you get to the
pump. It is normal for tires to heat
up and the air pressure inside to go
up as you drive.
2. Remove the cap from the valve
on one tire, then firmly press the
tire gauge onto the valve and
measure the pressure.
3. Add enough air to reach the
recommended air pressure.
Note:
If you overfill the tire, release
air by pressing on the metal stem
in the center of the valve. Then
recheck the pressure with your tire
gauge.
4. Replace the valve cap.
5. Repeat this procedure for each
tire, including the spare.
301
Wheels and Tires

Note:
Some spare tires operate at
a higher inflation pressure than the
other tires. For T type mini-spare
tires, see the Dissimilar spare wheel
and tire assembly information for
a description. Store and maintain
at 60 psi (4.15 bar). For full-size
and dissimilar spare tires, see the
Dissimilar spare wheel and tire
assembly information for a
description. Store and maintain at
the higher of the front and rear
inflation pressure as shown on the
Safety Compliance Certification
Label or Tire Label.
6. Visually inspect the tires to
make sure there are no nails or
other objects embedded that
could poke a hole in the tire and
cause an air leak.
7. Check the sidewalls to make
sure there are no gouges, cuts or
bulges.
Inspecting Your Tires and
Wheel Valve Stems
Periodically inspect the tire treads
for uneven or excessive wear and
remove objects such as stones,
nails or glass that could be
wedged in the tread grooves.
Check the tire and valve stems for
holes, cracks, or cuts that could
permit air leakage and repair or
replace the tire and replace the
valve stem. Inspect the tire
sidewalls for cracking, cuts,
bruises and other signs of damage
or excessive wear. If internal
damage to the tire is suspected,
have the tire dismounted and
inspected in case it needs to be
repaired or replaced. For your
safety, tires that are damaged or
show signs of excessive wear
should not be used because they
are more likely to blow out or fail.
Improper or inadequate vehicle
maintenance can cause tires to
wear abnormally. Inspect all your
tires, including the spare,
frequently, and replace them if
one or more of the following
conditions exist:
Tire Wear
E142546
When the tread is worn down to
one sixteenth of an inch (2
millimeters), tires must be
replaced to help prevent your
vehicle from skidding and
hydroplaning. Built-in treadwear
indicators, or wear bars, which
look like narrow strips of smooth
rubber across the tread will
appear on the tire when the tread
is worn down to one sixteenth of
an inch (2 millimeters).
302
Wheels and Tires
When the tire tread wears down
to the same height as these wear
bars, the tire is worn out and must
be replaced.
Damage
Periodically inspect the tire treads
and sidewalls for damage (such
as bulges in the tread or sidewalls,
cracks in the tread groove and
separation in the tread or
sidewall). If damage is observed
or suspected have the tire
inspected by a tire professional.
Tires can be damaged during
off-road use, so inspection after
off-road use is also
recommended.
Age
WARNING:
Tires degrade
over time depending on many
factors such as weather, storage
conditions, and conditions of use
(load, speed, inflation pressure)
the tires experience throughout
their lives.
WARNING:
In general, tires
should be replaced after six
years regardless of tread wear.
However, heat caused by hot
climates or frequent high loading
conditions can accelerate the
aging process and may require
tires to be replaced more
frequently.
WARNING:
You should
replace your spare tire when you
replace the road tires or after six
years due to aging even if it has
not been used.
U.S. DOT Tire Identification
Number
Both United States and Canada
Federal regulations require tire
manufacturers to place
standardized information on the
sidewall of all tires. This
information identifies and
describes the fundamental
characteristics of the tire and also
provides a U.S. DOT Tire
Identification Number for safety
standard certification and in case
of a recall.
This begins with the letters DOT
and indicates that the tire meets
all federal standards. The next
two numbers or letters are the
plant code designating where it
was manufactured, the next two
are the tire size code and the last
four numbers represent the week
and year the tire was built. For
example, the numbers 317 mean
the 31st week of 1997. After 2000
the numbers go to four digits. For
example, 2501 means the 25th
week of 2001. The numbers in
between are identification codes
used for traceability. This
information is used to contact
customers if a tire defect requires
a recall.
303
Wheels and Tires
Tire Replacement
Requirements
Your vehicle is equipped with tires
designed to provide a safe ride
and handling capability.
WARNING:
Only use
replacement tires and wheels
that are the same size, load
index, speed rating and type
(such as P-metric versus
LT-metric or all-season versus
all-terrain) as those originally
provided by Ford. The
recommended tire and wheel
size may be found on either the
Safety Compliance Certification
Label (affixed to either the door
hinge pillar, door-latch post, or
the door edge that meets the
door-latch post, next to the
driver's seating position), or the
Tire Label which is located on
the B-Pillar or edge of the
driver's door. If this information
is not found on these labels, then
you should contact your
authorized dealer as soon as
possible. Use of any tire or wheel
not recommended by Ford can
affect the safety and
performance of your vehicle,
which could result in an
increased risk of loss of vehicle
control, vehicle rollover, personal
injury and death.
WARNING:
To reduce the
risk of serious injury, when
mounting replacement tires and
wheels, you should not exceed
the maximum pressure indicated
on the sidewall of the tire to set
the beads without additional
precautions listed below. If the
beads do not seat at the
maximum pressure indicated,
re-lubricate and try again.
WARNING:
When inflating
the tire for mounting pressures
up to 20 psi (1.38 bar) greater
than the maximum pressure on
the tire sidewall, the following
precautions must be taken to
protect the person mounting the
tire:
•
Make sure that you have the
correct tire and wheel size.
•
Lubricate the tire bead and
wheel bead seat area again.
•
Stand at a minimum of 12 ft
(3.66 m) away from the wheel
and tire assembly.
•
Use both eye and ear
protection.
WARNING:
For a mounting
pressure more than 20 psi
(1.38 bar) greater than the
maximum pressure, a Ford
dealer or other tire service
professional should do the
mounting.
304
Wheels and Tires
WARNING:
Always inflate
steel carcass tires with a remote
air fill with the person inflating
standing at a minimum of 12 ft
(3.66 m) away from the wheel
and tire assembly.
Important:
Remember to replace
the wheel valve stems when the
road tires are replaced on your
vehicle.
The two front tires or two rear tires
should generally be replaced as a
pair, except if the vehicle is
equipped with four wheel drive.
Vehicles equipped with four wheel
drive should have all four tires
replaced simultaneously.
Unevenly worn tires, mismatched
makes, models or brands can be
different in size, resulting in
potential damage to the four
wheel drive system.
The tire pressure sensors mounted
in the wheels are not designed to
be used in aftermarket wheels.
The use of wheels or tires not
recommended by us could affect
the operation of your tire pressure
monitoring system.
If the tire pressure monitoring
system indicator is flashing, the
system is malfunctioning. Your
replacement tire might be
incompatible with your tire
pressure monitoring system, or
some component of the system
could be damaged.
Safety Practices
WARNING:
If your vehicle
is stuck in snow, mud or sand, do
not rapidly spin the tires;
spinning the tires can tear the
tire and cause an explosion. A
tire can explode in as little as
three to five seconds.
WARNING:
Do not spin the
wheels at over 34 mph
(55 km/h). The tires may fail and
injure a passenger or bystander.
Driving habits have a great deal
to do with your tire mileage and
safety.
*Observe posted speed limits
*Avoid fast starts, stops and turns
*Avoid potholes and objects on
the road
*Do not run over curbs or hit the
tire against a curb when parking
Highway Hazards
No matter how carefully you drive
there is always the possibility that
you could eventually have a flat
tire on the highway. Drive slowly
to the closest safe area out of
traffic. This could further damage
the flat tire, but your safety is
more important.
305
Wheels and Tires
If you feel a sudden vibration or
ride disturbance while driving, or
you suspect your tire or vehicle
has been damaged, immediately
reduce your speed. Drive with
caution until you can safely pull
off the road. Stop and inspect the
tires for damage. If a tire is
under-inflated or damaged,
deflate it, remove wheel and
replace it with your spare tire and
wheel. If you cannot detect a
cause, have the vehicle towed to
the nearest repair facility or tire
dealer to have the vehicle
inspected.
Tire and Wheel Alignment
A bad jolt from hitting a curb or
pothole can cause the front end
of your vehicle to become
misaligned or cause damage to
your tires. If your vehicle seems to
pull to one side when you are
driving, the wheels could be out of
alignment. Have an authorized
dealer check the wheel alignment
periodically.
Wheel misalignment in the front
or the rear can cause uneven and
rapid treadwear of your tires and
should be corrected by an
authorized dealer. Front-wheel
drive vehicles and those with an
independent rear suspension
could require alignment of all four
wheels.
The tires should also be balanced
periodically. An unbalanced tire
and wheel assembly could result
in irregular tire wear.
Tire Rotation
WARNING:
If the tire label
shows different tire pressures for
the front and rear tires and the
vehicle has a tire pressure
monitoring system, then you
need to update the settings for
the system sensors. Always
perform the system reset
procedure after tire rotation. If
you do not reset the system, it
may not provide a low tire
pressure warning when
necessary.
Note:
If your tires show uneven
wear ask an authorized dealer to
check for and correct any wheel
misalignment, tire imbalance or
mechanical problem involved
before tire rotation.
Note:
Your vehicle could be
equipped with a dissimilar spare
wheel and tire assembly. A
dissimilar spare wheel and tire
assembly is defined as a spare
wheel and tire assembly that is
different in brand, size or
appearance from the road tires and
wheels. If you have a dissimilar
spare wheel and tire assembly it is
intended for temporary use only
and should not be used in a tire
rotation.
Note:
After having your tires
rotated, inflation pressure must be
checked and adjusted to the
vehicle requirements.
306
Wheels and Tires
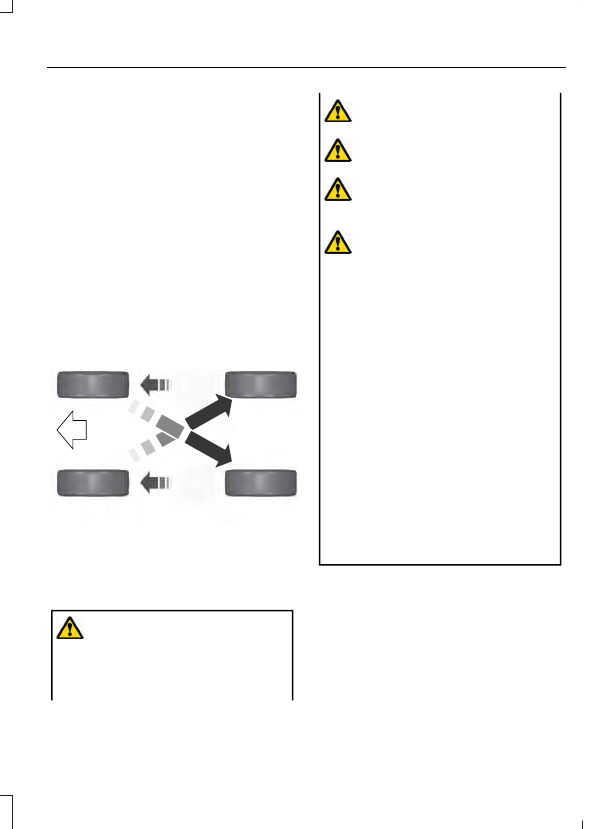
Note:
Uneven tread depth
between the front and rear tires
could lead to degradation in 4WD
engagement and disengagement
performance, additional noise from
the 4WD system or damage.
Rotating your tires at the
recommended interval (as
indicated in the Scheduled
Maintenance chapter) will help
your tires wear more evenly,
providing better tire performance
and longer tire life.
Rear-wheel drive vehicles and
four-wheel drive vehicles (front
tires at left of diagram)
E142548
Sometimes irregular tire wear can
be corrected by rotating the tires.
USING SNOW CHAINS
WARNING:
Do not exceed 30 mph
(50 km/h). Failure to follow this
instruction could result in the loss of
control of your vehicle, personal injury or
death.
WARNING:
Do not use snow chains
on snow-free roads.
WARNING:
Only fit snow chains to
specified tires.
WARNING:
If your vehicle is fitted
with wheel trims, remove them before
fitting snow chains.
WARNING:
Snow tires must be the
same size, load index and speed rating
as those originally provided by Ford. Use
of any tire or wheel not recommended
by Ford can affect the safety and
performance of your vehicle, which could
result in an increased risk of loss of
control, vehicle rollover, personal injury
and death. Additionally, the use of
non-recommended tires and wheels can
cause steering, suspension, axle, transfer
case or power transfer unit failure.
Follow the Ford recommended tire
inflation pressure found on the Safety
Compliance Certification Label (on the
door hinge pillar, door latch post or the
door edge that meets the door latch
post, next to the driver seat), or Tire
Label on the B-Pillar or the edge of the
driver door. Failure to follow the tire
pressure recommendations can cause
uneven treadwear patterns and
adversely affect the way your vehicle
handles.
Note:
The suspension insulation and
bumpers help prevent vehicle damage. Do
not remove these components from your
vehicle when using snow tires and chains.
307
Wheels and Tires
The tires on your vehicle have all-weather
treads to provide traction in rain and snow.
However, in some climates, you may need
to use snow tires and snow chains. If you
need to use snow chains, we recommend
you use steel wheels of the same size and
specifications, as snow chains may chip
aluminum wheels.
Note:
Only use snow chains on applicable
tire sizes.
Only fit snow chains to the following
specified tires:
•
255/70 R16 111T.
•
255/65 R17 110T.
•
265/65 R17 112T.
•
265/60 R18 110T.
•
LT265/65 R17 109T.
•
LT265/70 R17 112T.
Only use S-Class snow chains, 0.6 in
(15 mm) chain links.
Only use manual tensioning chains. Do not
use self-tensioning chains.
Only use snow chains in pairs on the rear
axle.
Note:
The anti-lock brake system continues
to operate normally.
Follow these guidelines when using snow
tires and chains:
•
If possible, avoid fully loading your
vehicle.
•
Install chains securely, verifying that
the chains do not touch any wiring,
brake lines, or fuel lines.
•
Drive cautiously. If you hear the chains
rub or bang against your vehicle, stop
and retighten the chains. If this does
not work, remove the chains to prevent
damage to your vehicle.
•
Remove the tire chains when you no
longer need them. Do not use tire
chains on dry roads.
If you have any questions regarding snow
chains, please contact your authorized
dealer.
Vehicles with Stability Control
When stability control is on, your vehicle
may exhibit some unusual driving
characteristics. To reduce this, switch
traction control off. See
TIRE PRESSURE MONITORING
SYSTEM
WARNING:
The tire pressure
monitoring system is not a substitute for
manually checking tire pressures. You
should periodically check tire pressures
using a pressure gauge. Failure to
correctly maintain tire pressures could
increase the risk of tire failure, loss of
control, vehicle rollover and personal
injury.
Note:
You should only use tire sealants in
roadside emergencies as they may cause
damage to the tire pressure monitoring
system sensor.
Note:
If the tire pressure monitoring system
sensor becomes damaged, it may not
function.
Each tire, including the spare (if
provided), should be checked
monthly when cold and inflated
to the inflation pressure recommended by
the vehicle manufacturer on the vehicle
placard or tire inflation pressure label. (If
your vehicle has tires of a different size
than the size indicated on the vehicle
placard or tire inflation pressure label, you
should determine the proper tire inflation
pressure for those tires).
308
Wheels and Tires

As an added safety feature, your vehicle
has been equipped with a Tire Pressure
Monitoring System (TPMS) that
illuminates a low tire pressure telltale
when one or more of your tires is
significantly under-inflated. Accordingly,
when the low tire pressure telltale
illuminates, you should stop and check
your tires as soon as possible, and inflate
them to the proper pressure. Driving on a
significantly under-inflated tire causes the
tire to overheat and can lead to tire failure.
Under-inflation also reduces fuel efficiency
and tire tread life, and may affect the
vehicle’s handling and stopping ability.
Please note that the TPMS is not a
substitute for proper tire maintenance, and
it is the driver’s responsibility to maintain
correct tire pressure, even if under-inflation
has not reached the level to trigger
illumination of the TPMS low tire pressure
telltale.
Your vehicle has also been equipped with
a TPMS malfunction indicator to indicate
when the system is not operating properly.
The TPMS malfunction indicator is
combined with the low tire pressure
telltale. When the system detects a
malfunction, the telltale will flash for
approximately one minute and then remain
continuously illuminated. This sequence
will continue upon subsequent vehicle
start-ups as long as the malfunction exists.
When the malfunction indicator is
illuminated, the system may not be able
to detect or signal low tire pressure as
intended. TPMS malfunctions may occur
for a variety of reasons, including the
installation of replacement or alternate
tires or wheels on the vehicle that prevent
the TPMS from functioning properly.
Always check the TPMS malfunction
telltale after replacing one or more tires or
wheels on your vehicle to ensure that the
replacement or alternate tires and wheels
allow the TPMS to continue to function
properly.
This device complies with Part 15 of the
FCC Rules and with License exempt RSS
Standards of Industry Canada. Operation
is subject to the following two conditions:
1.
This device may not cause harmful
interference, and
2. This device must accept any
interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired
operation.
WARNING:
Changes or
modifications not expressively approved
by the party responsible for compliance
could void the user's authority to operate
the equipment. The term "IC:" before the
radio certification number only signifies
that Industry Canada technical
specifications were met.
Changing Tires With a Tire
Pressure Monitoring System
E142549
Note:
Each road tire is equipped with a tire
pressure sensor located inside the wheel
and tire assembly cavity. The pressure
sensor is attached to the valve stem. The
pressure sensor is covered by the tire and is
not visible unless the tire is removed. Take
care when changing the tire to avoid
damaging the sensor.
You should always have your tires serviced
by an authorized dealer.
309
Wheels and Tires

Check the tire pressure periodically (at
least monthly) using an accurate tire
gauge. See
When Inflating Your Tires
in
this chapter.
Understanding Your Tire Pressure
Monitoring System
E250820
The tire pressure monitoring system
measures pressure in your road tires and
sends the tire pressure readings to your
vehicle. You can view the tire pressure
readings through the information display.
See
low tire pressure warning light will turn on
if the tire pressure is significantly low. Once
the light is illuminated, your tires are
under-inflated and need to be inflated to
the manufacturer’s recommended tire
pressure. Even if the light turns on and a
short time later turns off, your tire pressure
still needs to be checked.
When Your Temporary Spare Tire is
Installed
When one of your road tires needs to be
replaced with the temporary spare, the
system will continue to identify an issue to
remind you that the damaged road wheel
and tire assembly needs to be repaired and
put back on your vehicle.
To restore the full function of the tire
pressure monitoring system, have the
damaged road wheel and tire assembly
repaired and remounted on your vehicle.
When You Believe Your System is Not
Operating Properly
The main function of the tire pressure
monitoring system is to warn you when
your tires need air. It can also warn you in
the event the system is no longer capable
of functioning as intended. See the
following chart for information concerning
your tire pressure monitoring system:
310
Wheels and Tires

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст