Mazda Training manual — part 251
6 – COOLING SYSTEM
89
Piston Engine Fundamentals
TC010-05-01S
REVIEW EXERCISE 8
Fill in the words that correctly complete these sentences. Check your answers with the
answer key on page 91.
1. Coolant lowers the freezing point of water and ______________________ the boiling
point.
2. The _____________________ helps the engine warm up by restricting coolant flow
until a certain temperature is reached.
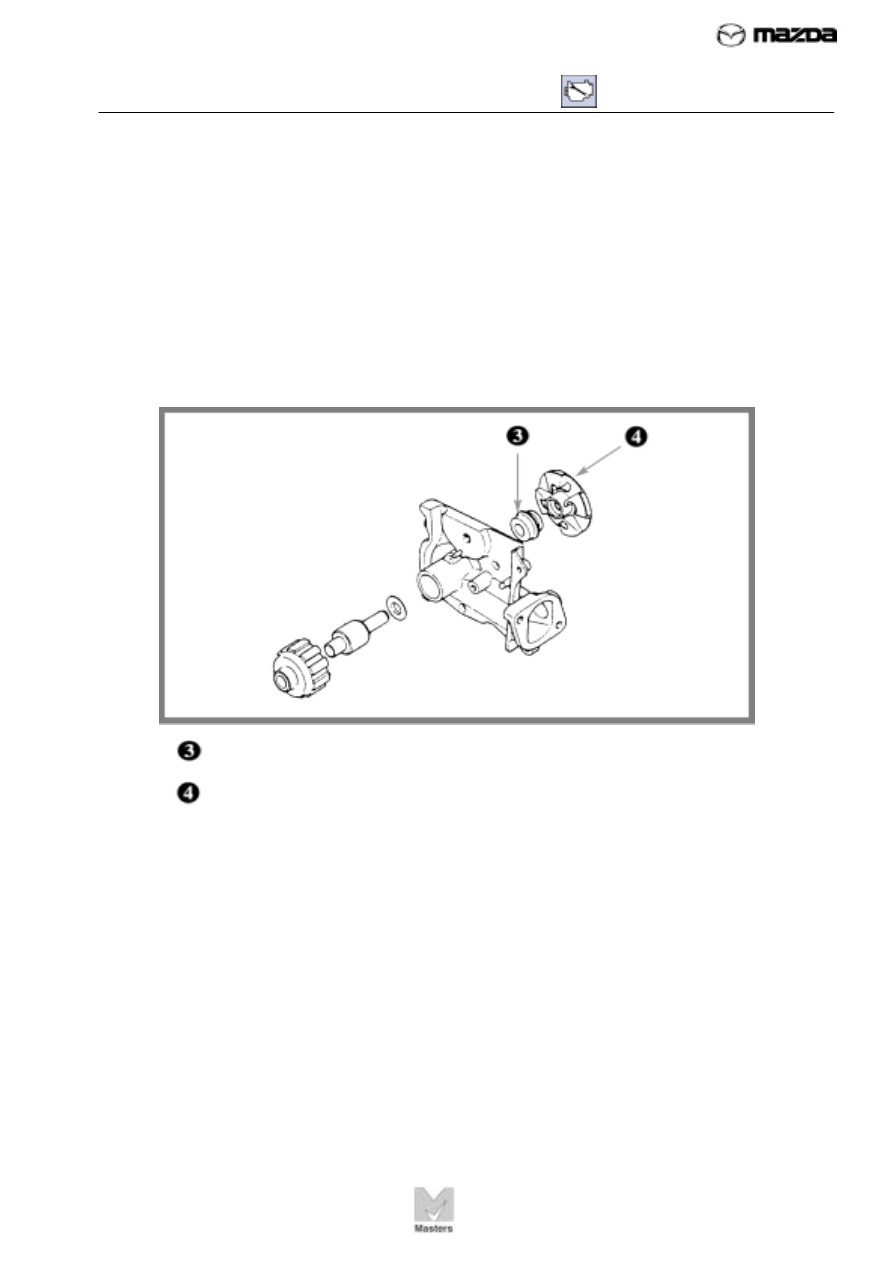
Use the water pump illustration below to complete the following two items.
3. Item in this illustration is the _______________________.
4. Item in this illustration is the _______________________.
5. Which of these symptoms would you expect to find in an engine that has a failing
water pump? More than one answer may be correct.
A. overheating
B. noisy tappets
C. hard starting
D. gasoline fumes
6 – COOLING SYSTEM
90
Piston Engine Fundamentals
TC010-05-01S
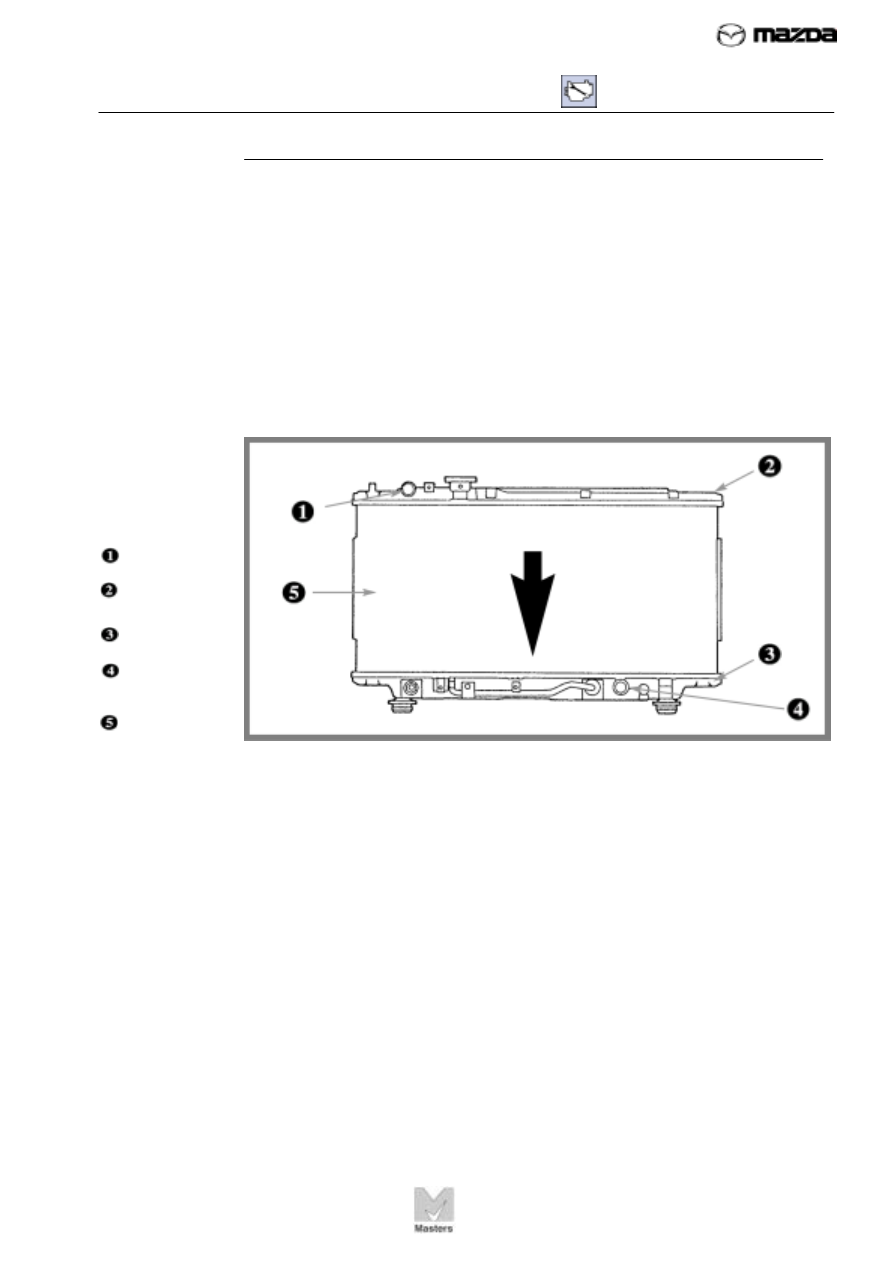
FIGURE 60. A
downflow-type
radiator has an
upper and lower
tank.
Coolant inlet
Upper tank
Lower tank
Coolant
outlet
Core
RADIATORS
Mazda uses both downflow and crossflow radiators.
Downflow-Type
Figure 60 shows a typical downflow-type radiator. As its name suggests,
the downflow radiator has an upper and lower tank. Tubes connect the
tanks. Coolant flows down from the upper tank through the core and into
the lower tank. Cooling takes place as the liquid passes through the
radiator core. If the vehicle has an automatic transmission, the radiator
may have a separate cooler at the bottom for the automatic transmission
fluid.
Coolant Flow
6 – COOLING SYSTEM
91
Piston Engine Fundamentals
TC010-05-01S
Crossflow-Type
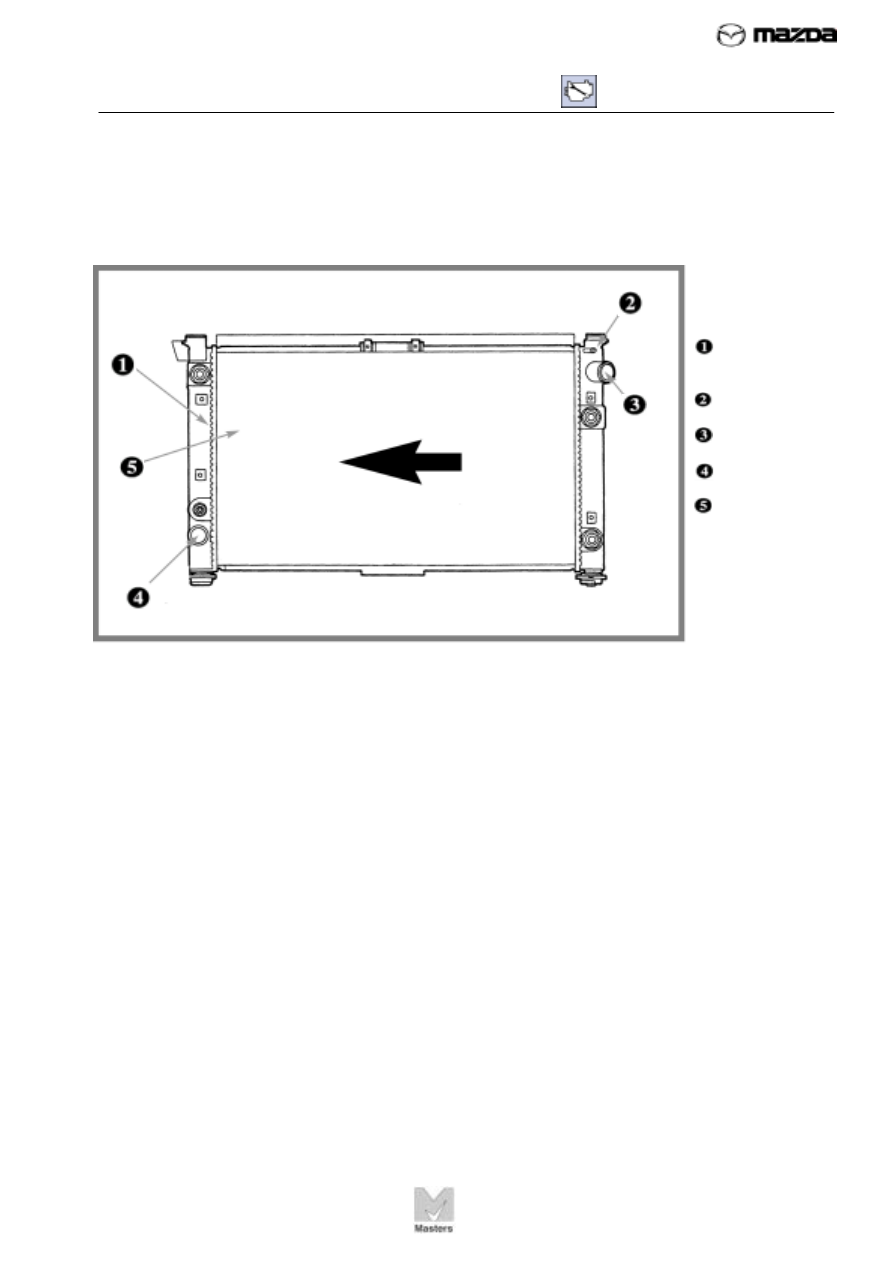
The crossflow-type radiator is also commonly used. In this design
(shown in Figure 61), the tanks are on the side of the core, so the
coolant flows through tubes from one side to the other.
FIGURE 61. A
crossflow-type
radiator has side
tanks.
Right tank
Left tank
Coolant inlet
Coolant outlet
Core
Answers to
Review Exercise
8
1. lowers
2. thermostat
3. water seal
4. impeller
5. A — over-
heating
Coolant Flow
6 – COOLING SYSTEM
92
Piston Engine Fundamentals
TC010-05-01S
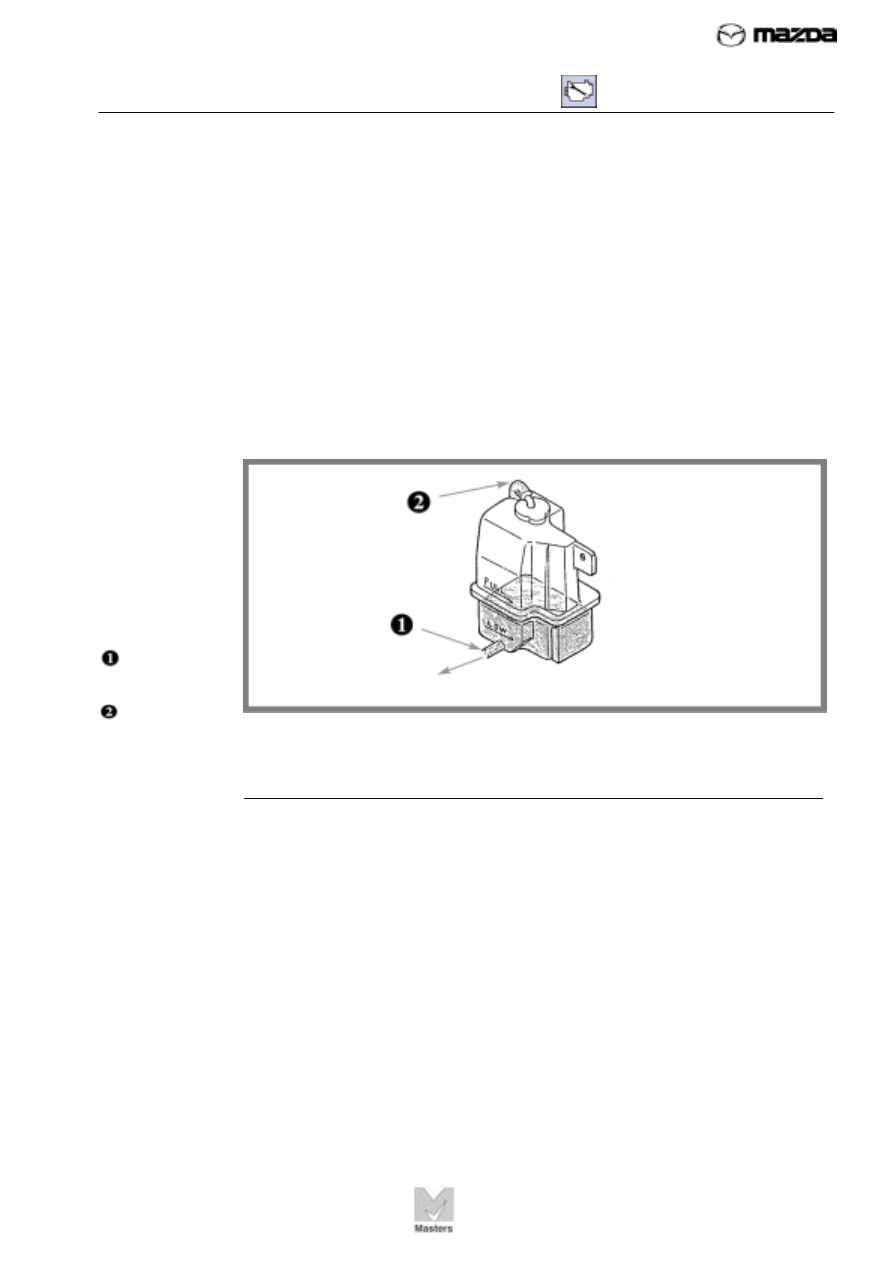
FIGURE 62. As
the coolant
expands, the
excess coolant
flows into the
reservoir. As it
contracts, it is
drawn back into
the radiator.
Radiator
reservoir hose
Overflow tube
Radiator Reservoir
Coolant level is checked and coolant is added at the radiator reservoir. A
hose connects the reservoir to the radiator filler neck, as shown in Figure
62. As engine temperature rises, the expanding coolant flows from the
radiator into the reservoir. When the engine is stopped, the coolant
temperature drops and contracts. A partial vacuum develops in the
cooling system, drawing coolant from the reservoir backinto the cooling
system.
As shown in Figure 62, the reservoir has an overflow tube that allows
coolant to escape if the cooling system is overfilled or when the engine
overheats.
PRESSURE CAP
The pressure cap on the radiator maintains pressure in the cooling
system. The boiling point of a liquid rises with the amount of pressure it is
under. For example, water at sea level boils at about 212 degrees
Fahrenheit. Water in a typical pressurized cooling system boils at more
than 250 degrees Fahrenheit. So pressurizing the cooling system
effectively raises the operating temperature of the engine.
Figure 63 shows a typical radiator pressure cap, which fits on the filler
neck on the radiator. The cap includes a pressure valve (or blow-off
valve) and a vacuum valve. Both are spring-loaded to remain closed
when the system is within operating ranges.
To filler neck

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст