Lexus ES300 (2002 year). Service manual — part 134

ENGINE – 1MZ-FE ENGINE
EG-27
206EG19
206EG18
Yoke
Armature
Brush
Armature
Surface
Commutator
Permanent Magnet
Brush
Length
STARTING SYSTEM
Starter
1) General
A compact and lightweight PS (Planetary reduction-Segment conductor motor) starter has been
adopted on all models.
Because the PS starter contains an armature that uses square-shaped conductors, and its surface func-
tions as a commutator, it has resulted in both improving its output torque and reducing its overall
length.
In place of the field coil used in the conventional starter, the PS starter uses two types of permanent
magnets: main magnets and interpolar magnets. The main magnets and interpolar magnets have been
efficiently arranged to increase the magnetic flux and to shorten the length of the yoke.
Specifications
Model
PS Starter
Conventional Type Starter
Length
128 mm (5.04 in.)
145 mm (5.71 in.)
Weight
2950 g
3800 g
Rating Voltage
12 V
12 V
Rating Output
1.6 kW
1.4 kW
Rotating of Direction
Counterclockwise*
*: Viewed from Pinion Side

ENGINE – 1MZ-FE ENGINE
EG-28
206EG20
Conventional Type Starter
PS Starter
Armature
A
A
B
B
Armature
Brush
Commutator
Brush
Surface
Commutator
Square-Shaped
Conductor
Round-Shaped
Conductor Wire
A – A Cross Section
PS Starter
B – B Cross Section
Conventional Type
206EG21
Cross Section of Yoke
Main Magnets
Yoke
Interpolar Magnets
Magnetic Flux Generated
by Main Magnets
Magnetic Flux Generated by
Relationship Between Main
Magnets
Armature
2) Construction
Instead of the construction of the armature coil of the conventional starter that uses round-shaped con-
ductor wires, the PS starter uses square conductors. With this type of construction, the same conditions
that are realized by winding numerous round-shaped conductor wires can be achieved without increas-
ing the mass. As a result, the output torque has been increased, and the armature coil has been made
more compact.
Because the surface of the square-shaped conductors that are used in the armature coil functions as
a commutator, the overall length of the PS starter has been shortened.
Instead of the field coils used in the conventional starter, the PS starter has adopted two types of perma-
nent magnets: the main magnets and the interpolar magnets. The main and interpolar magnets are ar-
ranged alternately inside the yoke, allowing the magnetic flux that is generated between the main and
interpolar magnets to be added to the magnetic flux that is generated by the main magnets.
In addition to increasing the amount of magnetic flux, this construction shortens the overall length of
the yoke.

ENGINE – 1MZ-FE ENGINE
EG-29
211EG11
Torque Rod
Right Mount
(Hydraulic
Engine Mount)
Active Control
Engine Mount
Left Mount
(Hydraulic
Engine Mount)
211EG31
Intake Air Chamber
Vacuum
Tank
Engine
VSV
ECM
Active Control
Engine Mount
Side Branch
Main Liquid
Chamber
Diaphragm
Air
Chamber
Rubber
161ES46
ENGINE MOUNT
1. General
A 3-point support on the front subframe has been
adopted. An active control engine mount has been
adopted on the front engine mount and a hydraulic
engine mount has been adopted on the right and
left engine mounts to realize low noise and vibra-
tion and to achieve high levels of both riding com-
fort and drivability.
2. Active Control Engine Mount
The operating range of the active control engine mount is during idling under the engine speeds of 900 rpm.
Signals that are synchronized to the engine rpm are sent by the ECM to the VSV and the engine vacuum is
utilized to vary the pressure of the intake air chamber in the active control engine mount. As a result, the dia-
phragm vibrates, and using the liquid as a medium, the rubber mount vibrates.
This vibration of the engine mount acts to cancel out the engine vibration during idle, thus reducing the vibra-
tion and noise at idle.
The engine mount’s damping force to generate vibrations is adjusted through the effects of the orifice and
the side branch.
ENGINE – 1MZ-FE ENGINE
EG-30
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
1. General
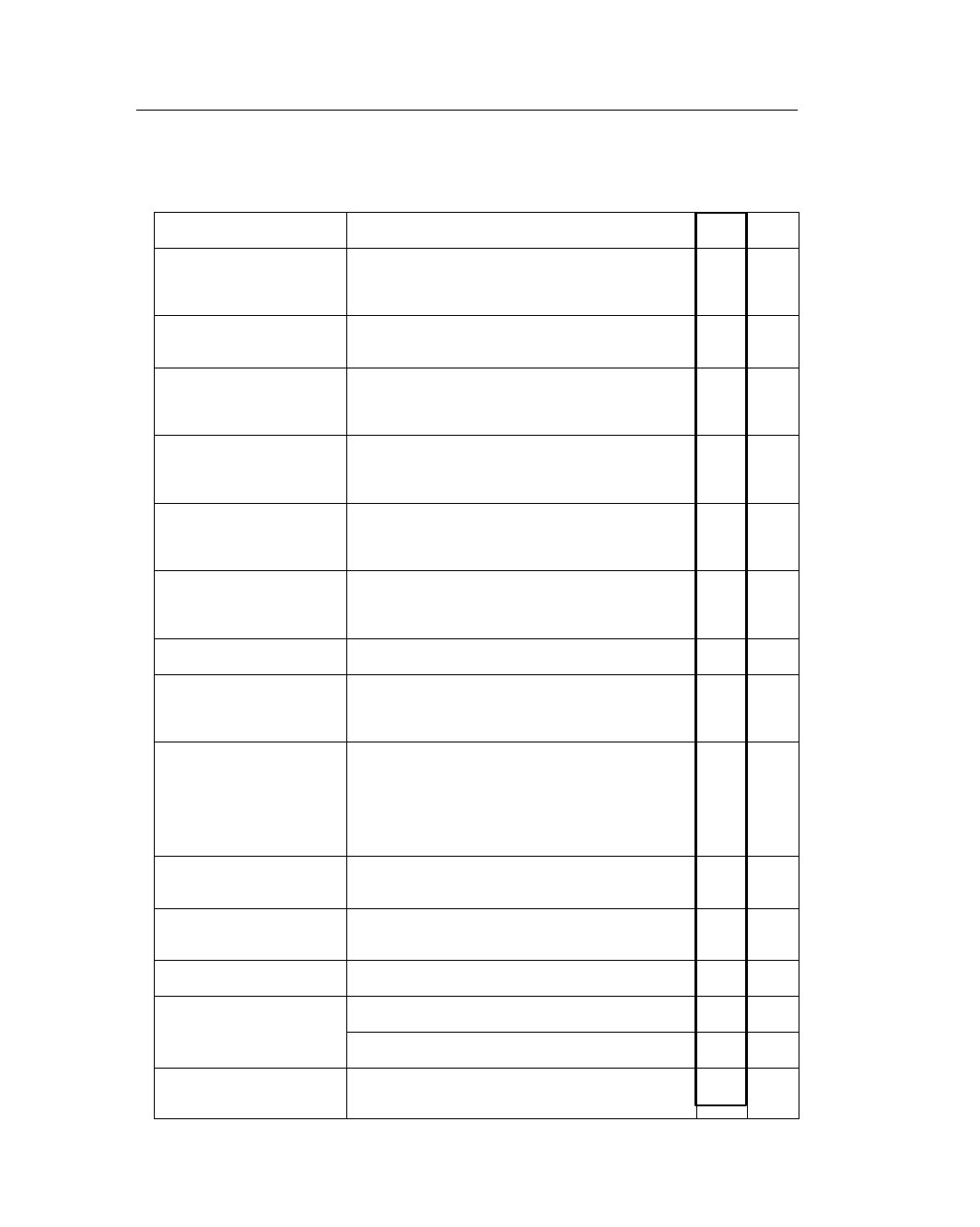
The engine control system of the 1MZ-FE engine has following system.
System
Outline
’02
ES300
’01
ES300
SFI
(Sequential Multiport
Fuel Injection)
(For details, see page EG-38)
An L-type SFI system directly detects the intake air
mass with a hot wire type mass air flow meter.
ESA
(Electronic Spark Advance)
(For details, see page EG-38)
Ignition timing is determined by the ECM based on
signals from various sensors. The ECM corrects
ignition timing in response to engine knocking.
ETCS-i
(Electronic Throttle
Control System-intelligent)
(For details, see page EG-39)
Optimally controls the throttle valve opening in
accordance with the amount of accelerator pedal effort
and the condition of the engine and the vehicle.
—
VVT-i
(Variable Valve
Timing-intelligent)
(For details, see page EG-41)
Controls the intake camshaft to an optimal valve timing
in accordance with the engine condition.
ACIS
(Acoustic Control
Induction System)
(For details, see page EG-42)
The intake air passages are switched according to the
engine speed and throttle valve opening angle to provide
high performance in all speed ranges.
Air Intake Control
System
(For details, see page EG-46)
The intake air duct is divided into two areas, and the
ECM controls the air intake control valve and the
actuator that are provided in one of the areas to reduce
the amount of engine noise.
—
Fuel Pump Control
Fuel pump operation is controlled by signal from the
ECM.
Air Fuel Ratio Sensor,
Oxygen Sensor
Heater Control
Maintains the temperature of the air fuel ratio sensor or
oxygen sensor at an appropriate level to increase
accuracy of detection of the oxygen concentration in the
exhaust gas.
Evaporative
Emission Control
(For details, see page EG-47)
The ECM controls the purge flow of evaporative
emission (HC) in the charcoal canister in accordance
with engine conditions.
Using 3 VSVs and a vapor pressure sensor, the ECM
detects any evaporative emission leakage occurring
between the fuel tank and the charcoal canister
through the changes in the tank pressure.
Active Control Engine
Mount
(For details, see page EG-29)
The damping characteristic of the front engine mount is
controlled variably to reduce idling vibration.
Air Conditioning
Cut-off Control
By turning the air conditioner compressor ON or OFF
in accordance with the engine condition, drivability is
maintained.
Engine Immobiliser
Prohibits fuel delivery and ignition if an attempt is made
to start the engine with an invalid ignition key.
Diagnosis
When the ECM detects a malfunction, the ECM
diagnoses and memorizes the failed section.
Diagnosis
(For details, see page EG-52)
To increase the speed for processing the signals, the
32-bit CPU of the ECM has been adopted.
—
Fail-Safe
(For details, see page EG-53)
When the ECM detects a malfunction, the ECM stops or
controls the engine according to the data already stored
in the memory.

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст