Lexus ES300 (2002 year). Service manual — part 120
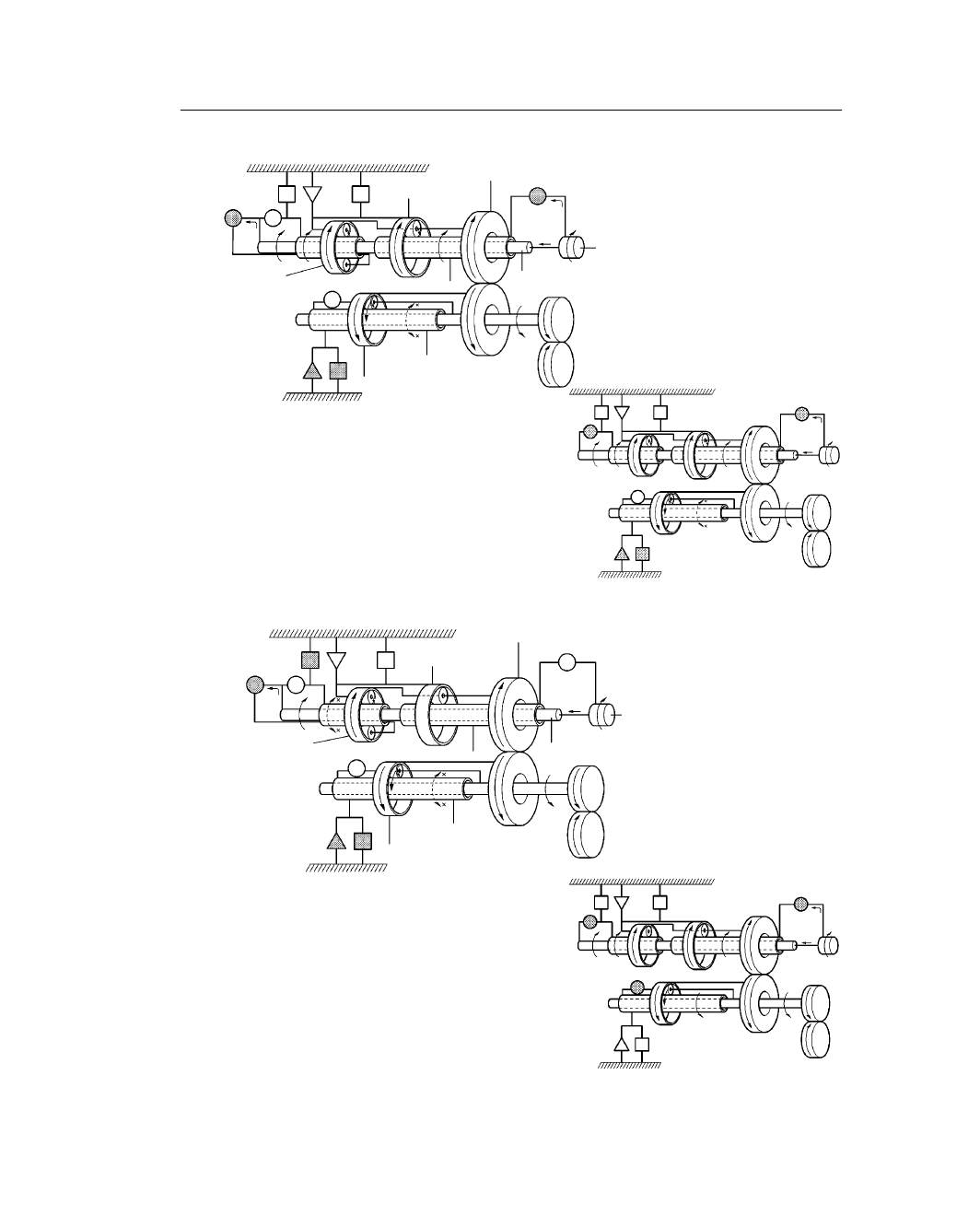
CHASSIS – U150E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-9
211CH06
U150E
U140E
Counter Drive Gear
Front Planetary Gear
Input Shaft
Rear Planetary Gear
Sun Gear
Intermediate Shaft
Differential Drive
Pinion
Sun Gear
U / D Planetary Gear
Ring Gear
B
1
F
1
B
2
C
0
C
2
C
1
C
3
F
2
B
3
211CH58
U150E
U140E
Counter Drive Gear
Front Planetary Gear
Input Shaft
Rear Planetary Gear
Sun Gear
Intermediate Shaft
Differential Drive
Pinion
Sun Gear
U / D Planetary Gear
Ring Gear
B
1
F
1
B
2
C
0
C
2
C
1
C
3
F
2
B
3
211CH07
211CH59
3rd Gear
4th Gear
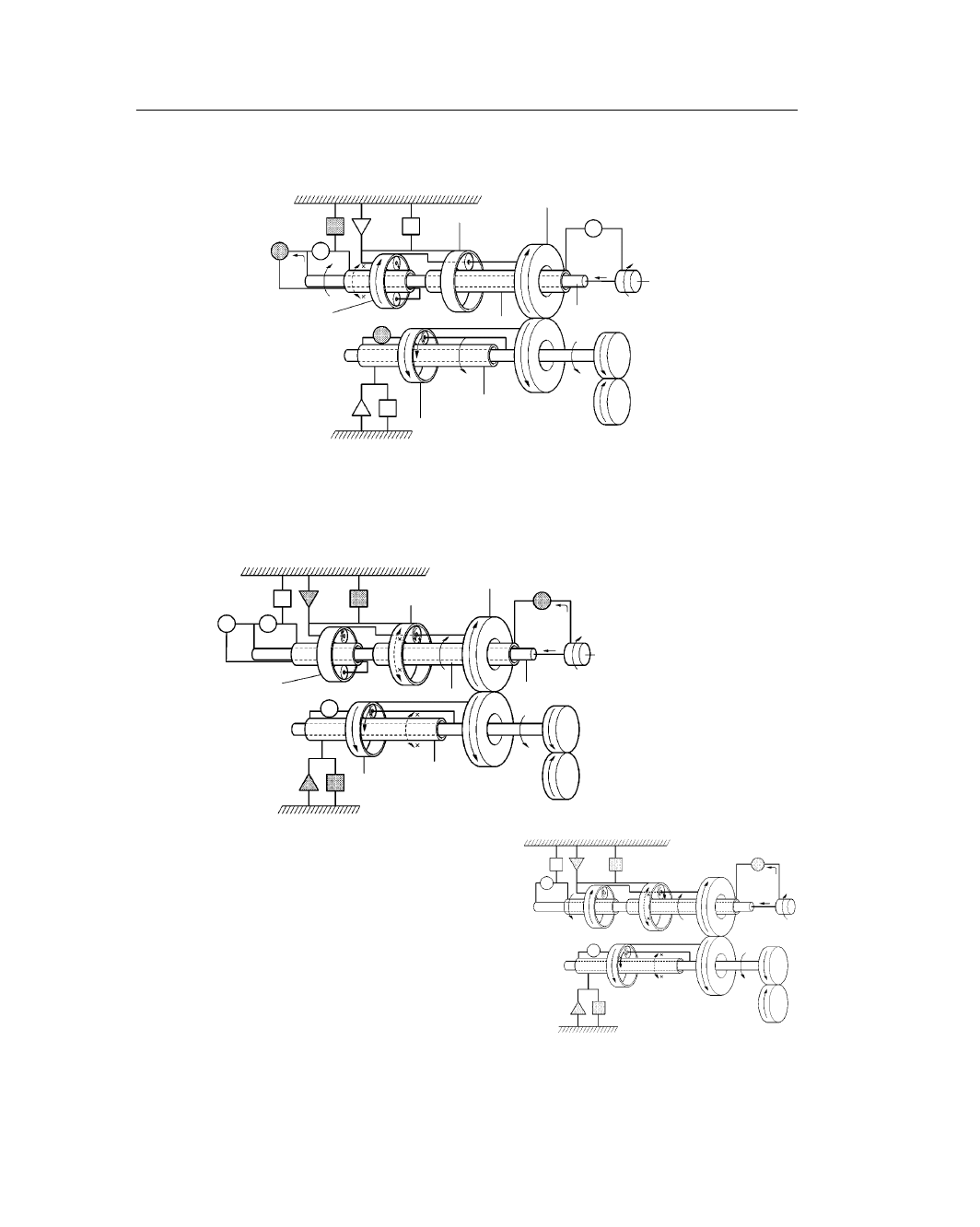
CHASSIS – U150E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-10
211CH08
Counter Drive Gear
Front Planetary Gear
Input Shaft
Rear Planetary Gear
Sun Gear
Intermediate Shaft
Differential Drive
Pinion
Sun Gear
U / D Planetary Gear
Ring Gear
B
1
F
1
B
2
C
0
C
2
C
1
C
3
F
2
B
3
161ES13
U150E
U140E
Counter Drive Gear
Front Planetary Gear
Input Shaft
Rear Planetary Gear
Sun Gear
Intermediate Shaft
Differential Drive
Pinion
Sun Gear
U / D Planetary Gear
Ring Gear
B
1
F
1
B
2
C
0
C
2
C
1
C
3
F
2
B
3
211CH09
5th Gear
1st Gear (L Position)
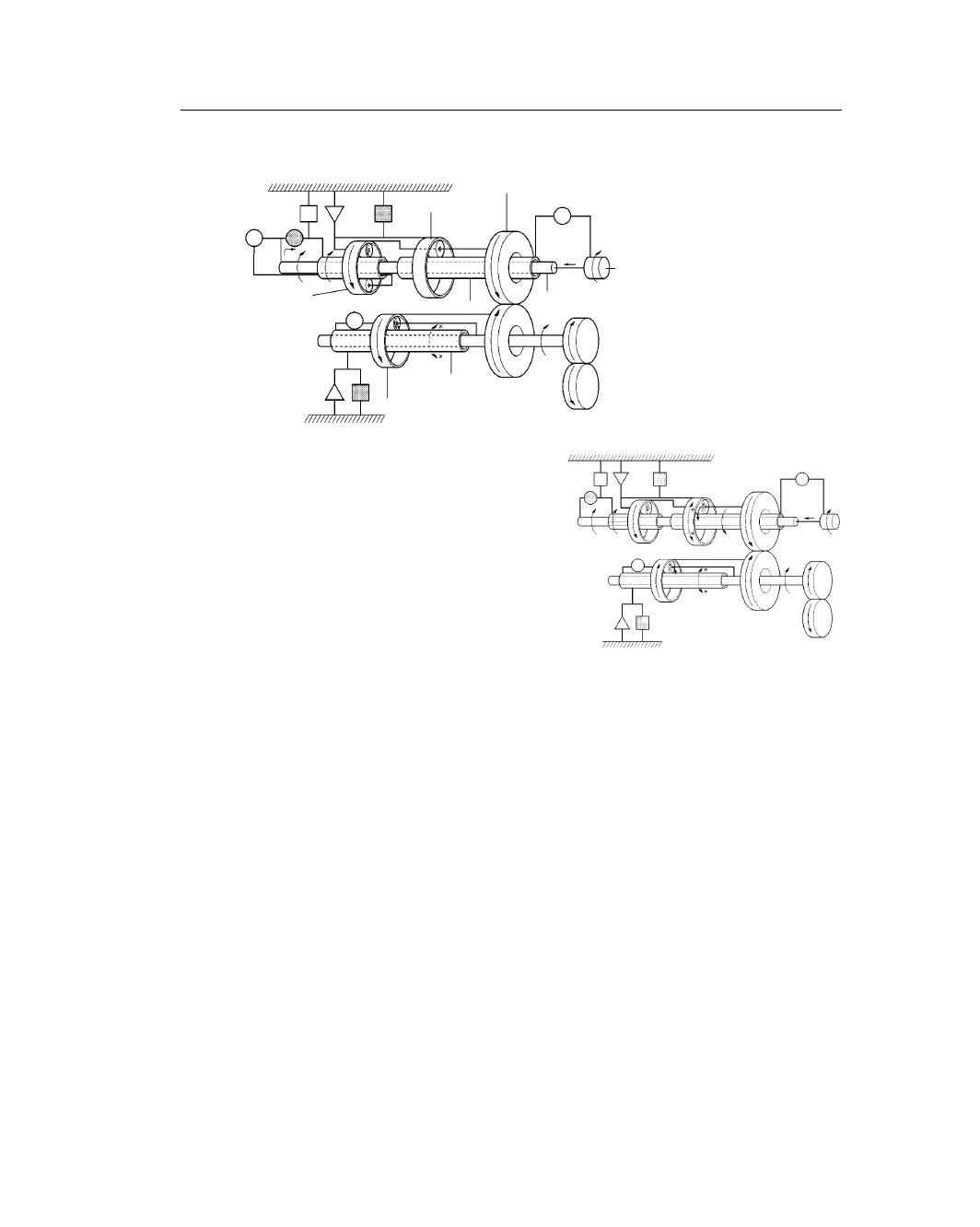
CHASSIS – U150E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-11
211CH10
U150E
U140E
Front Planetary Gear
Counter Drive Gear
Input Shaft
Rear Planetary Gear
Sun Gear
Intermediate Shaft
Differential Drive
Pinion
Sun Gear
U / D Planetary Gear
Ring Gear
B
1
F
1
B
2
C
0
C
2
C
1
C
3
F
2
B
3
181CH66
Reverse Gear (R Position)

CHASSIS – U150E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-12
211CH11
C
0
Clutch
Piston
Chamber A
Chamber B
C
0
Clutch
C
2
Clutch
C
1
Clutch
C
3
Clutch
157CH17
Fluid pressure
applied to piston
Centrifugal fluid pressure
applied to chamber B
Target fluid pressure
(original clutch pressure)
—
=
Target Fluid Pressure
Centrifugal Fluid Pressure
Applied to the Chamber A
Clutch
Centrifugal Fluid Pressure
Applied to Chamber B
Chamber B
(Lubrication Fluid)
Piston Fluid
Pressure
Chamber
Fluid Pressure
Applied to Piston
Shaft Side
4. Centrifugal Fluid Pressure Canceling Mechanism
There are two reasons for improving the conventional clutch mechanism:
To prevent the generation of pressure by the centrifugal force that applied to the fluid in piston fluid
pressure chamber (hereafter referred to as “chamber A”) when the clutch is released, a check ball is
provided to discharge the fluid. Therefore, before the clutch can be subsequently applied, it took time for
the fluid to fill the chamber A.
During shifting, in addition to the original clutch pressure that is controlled by the valve body, the pressure
that acts on the fluid in the chamber A also exerts influence, which is dependent upon revolution fluctua-
tions.
To address these two needs for improvement, a canceling fluid pressure chamber (hereafter referred to as
“chamber B”) has been provided opposite chamber A.
By utilizing the lubrication fluid such as that of the shaft, the same amount of centrifugal force is applied,
thus canceling the centrifugal force that is applied to the piston itself. Accordingly, it is not necessary to
discharge the fluid through the use of a check ball, and a highly responsive and smooth shifting characteristic
has been achieved.

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст